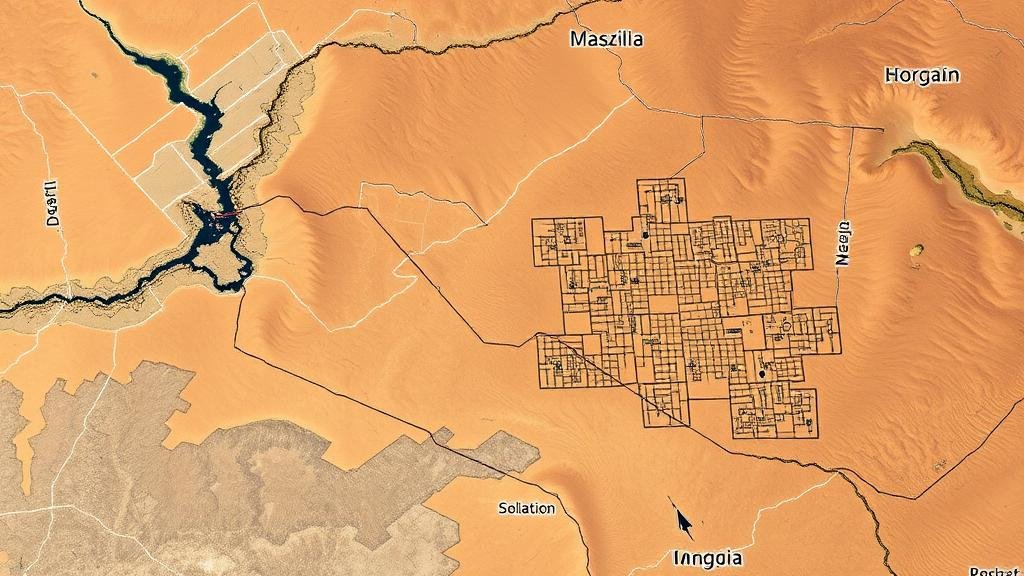
Using satellite imaging to uncover hidden city grids in Mongolia’s Gobi Desert.
Using Satellite Imaging to Uncover Hidden City Grids in Mongolia’s Gobi Desert
The Gobi Desert, a vast expanse covering parts of northern China and southern Mongolia, is often viewed as a remote and desolate region. But, recent studies employing satellite imaging technology have revealed significant evidence of ancient urban settlements and city grids that have been obscured by the deserts shifting sands. This article explores how satellite imaging has unearthed these hidden grids and the implications of such discoveries.
The Significance of Satellite Imaging
Satellite imaging has transformed archaeological methods, allowing researchers to observe large and inaccessible areas without physical excavation. Technologies such as remote sensing, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and high-resolution optical imagery enable scientists to identify patterns and structures that indicate human habitation in the past.
For example, in 2021, a collaborative effort between Mongolian archaeologists and international satellites led to the detection of previously unidentified city layouts beneath the Gobis surface. By capturing different wavelengths of light, these technologies can distinguish subtle changes in vegetation, soil, and topography, indicating human activity.
Notable Discoveries in the Gobi Desert
One of the most remarkable discoveries was made near the ancient Silk Road, where satellite imaging revealed remnants of a large urban grid that is believed to date back to the Yayoi period (300 BCE – 300 CE). This period was marked by extensive trade routes across Asia, making it plausible that significant urban centers would emerge in strategic locations.
- Structures resembling city walls and roads were detected, indicating organized planning.
- Evidence of agricultural terracing was found, suggesting that these communities were capable of sustaining a significant population.
Technological Innovations in Archaeology
Remote sensing technologies have not only advanced our understanding of the spatial arrangement of ancient cities but also provided insights into other elements such as:
- Geographical Context: Understanding how ancient societies adapted to their arid environment.
- Trade Networks: Mapping connections between cities that facilitated commerce.
- Cultural Exchange: Identifying areas rich in cultural artifacts based on satellite-detectable sites.
These discoveries highlight the complexity of ancient urbanization and the previously underestimated human impact on the Gobi Deserts landscape.
Challenges and Limitations
While satellite imaging has opened new avenues in archaeological research, it is not without limitations. resolution of images may not always be sufficient to distinguish smaller structures, and interpretations can vary based on the quality of data. Also, environmental factors like dust storms can obscure the view and hamper analysis.
- Data Resolution: High-resolution satellite images are critical for detailed analysis, yet often costly and not readily available.
- Ground Truthing: Confirming findings from satellite data requires ground verification, which can be logistically challenging.
The Future of Archaeology in the Gobi
Looking forward, the integration of artificial intelligence with satellite imaging is expected to enhance the discovery process. Algorithms can automatically identify patterns that human eyes might miss, leading to faster and more efficient archaeological surveys.
Mongolian researchers are optimistic that the continuing advancement of these technologies will lead to a more profound understanding of cultural history not only in the Gobi Desert but throughout Central Asia.
Actionable Takeaways
Understanding the historical significance of the Gobi Desert and similar regions can pave the way for fostering greater cultural appreciation and heritage conservation efforts. Key takeaways include:
- Support and invest in satellite technologies for archaeological applications.
- Encourage interdisciplinary collaborations between technology developers and archaeologists.
- Promote educational programs on the importance of preserving historical sites revealed by new technologies.
Through continued exploration and technological innovation, the hidden city grids of Mongolia’s Gobi Desert may shed light on ancient civilizations, enhancing our understanding of human history in one of the worlds most enigmatic landscapes.