Spotting Unique Bone Artifacts in Cave Deposits From Early Habitations
Spotting Unique Bone Artifacts in Cave Deposits From Early Habitations
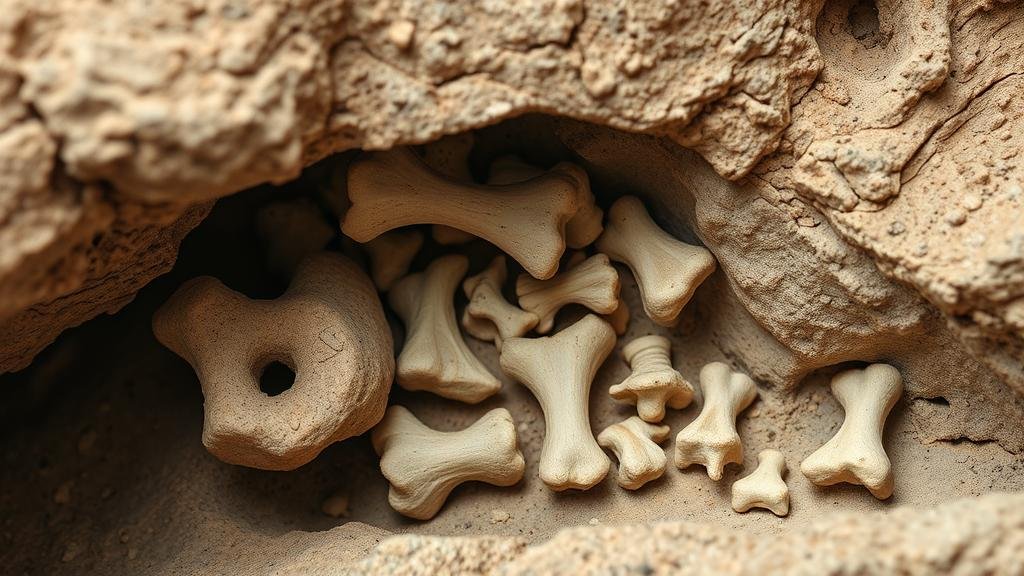
The study of early human habitation often includes an exploration of cave deposits, where unique bone artifacts can provide substantial insights into the lifestyles, diets, and cultures of our ancestors. Detecting and analyzing these artifacts requires a meticulous approach to excavation and research methodologies. This article delves into the methods for spotting these distinct bone artifacts, their significance, and notable case studies that highlight their implications in archaeological research.
Understanding Cave Deposits
Cave deposits, also known as speleothems, form over millennia and often contain layers of sediment that encapsulate artifacts left by ancient occupants. composition of these deposits can vary greatly depending on environmental factors and the activities of the inhabitants. Typically, these layers consist of:
- Organic materials such as bones and plant remains
- Inorganic materials including rocks and minerals
- Depositional layers that can reveal chronological sequences of habitation
Stratigraphy–the study of rock layers–plays a crucial role in excavating these deposits. By understanding the stratigraphic context, researchers can deduce the relative ages of artifacts and their cultural significance. For example, the presence of animal bones alongside stone tools may indicate hunting practices or dietary habits of the early humans who inhabited the cave.
Methods for Spotting Unique Bone Artifacts
Identifying unique bone artifacts requires a blend of fieldwork expertise and laboratory analysis. The following methods are integral to the process:
- Visual Inspection: Early-stage visual assessments help archaeologists recognize bone fragments amid soil and sediment. Key features include texture, color, and bone morphology, which can distinguish animal bones from modern debris.
- Stratigraphic Excavation: Carefully planned excavations in stratified deposits minimize disturbance to the matrix and allow for the identification of unique artifacts within their respective layers.
- Bone Identification Techniques: Techniques such as comparative anatomy, where modern species’ skeletal systems are compared to fossilized remains, facilitate accurate identification of the species from which the bone originated.
- Radiocarbon Dating: This method is essential for establishing timelines for bone artifacts. It can provide insights into when the artifacts were last used or deposited.
Significance of Bone Artifacts
Bone artifacts serve several crucial functions in understanding early human life. Some of the key aspects include:
- Dietary Analysis: The types of animal bones found in a cave can reveal the diet of early humans. For example, bones that show cut marks from tools indicate that the animals were processed for food.
- Cultural Practices: Unique bone artifacts, such as those that have been shaped or carved, may symbolize ritualistic usage or artistic expression.
- Environmental Adaptations: The selection of specific animals–some of which may now be extinct–can provide insights into how early humans adapted to their environment.
Case Studies: Notable Discoveries
Several archaeological sites have yielded significant finds that enhance our understanding of early human habitation. One notable example is the Grotte de Font-de-Gaume in France, where detailed analyses of bison bones have revealed the hunting practices of early Cro-Magnon populations. The presence of bone fragments with specific cut patterns indicates organized hunting strategies and communal efforts in food acquisition.
Another example can be drawn from the Lascaux cave system, also in France. The discovery of bones of young horses alongside intricate cave paintings offers clues about the relationship between early humans and their prey, establishing a connection between hunting strategies and cultural expressions.
Real-World Applications
The field of archaeological research relies on the understanding gained from unique bone artifacts. This knowledge is instrumental in:
- Conservation Efforts: Insights into past human behaviors can inform modern conservation strategies for both cave sites and animal species.
- Educational Programs: Findings are often used to enrich educational materials in museums and schools, offering tangible connections to historical ecology and anthropology.
- Policy Development: Understanding ancient practices informs policies on land use, wildlife preservation, and archaeological site protection.
Actionable Takeaways
For researchers and enthusiasts interested in the field of archaeology and the study of early human habitation:
- Embrace a multidisciplinary approach, combining natural sciences and anthropology to enrich your understanding of bone artifacts.
- Engage with local archaeological societies to further your education and participation in excavations.
- Stay updated on technological advancements in dating techniques and data analysis, as these can significantly enhance artifact identification and analysis.
In summary, spotting unique bone artifacts in cave deposits is a pivotal aspect of understanding early human habits and cultures. Through stratigraphic excavation, visual inspections, and advanced analysis, researchers can extract invaluable information far beyond the artifacts themselves, illuminating the intricate tapestry of human history.