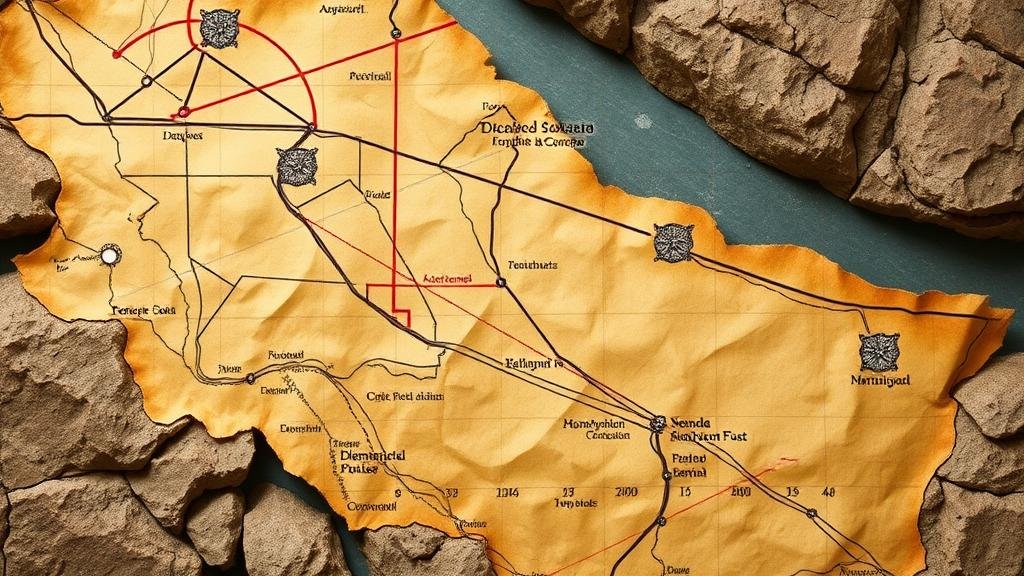
Reading Rock Alignment Diagrams Found in Spanish Treasure Maps
Understanding Reading Rock Alignment Diagrams in Spanish Treasure Maps
Spanish treasure maps, particularly those attributed to the era of exploration and colonial conquest, are steeped in mystery and intrigue. Among their numerous features, reading rock alignment diagrams stands out as a complex yet fascinating aspect that can guide treasure hunters and historians alike. This article delves into the nature of these diagrams, their significance, and how to interpret them effectively.
The Historical Context of Spanish Treasure Maps
To appreciate the significance of rock alignment diagrams found in Spanish treasure maps, it is essential to understand the historical context in which these maps were created. During the Age of Exploration, particularly in the 16th to 18th centuries, Spanish explorers sought gold, silver, and other valuable resources in the New World. Maps were crucial for navigation and often contained encoded information to protect treasures from rivals.
Key Components of Spanish Treasure Maps
- Iconography: These maps often feature unique symbols that indicate various landmarks or treasures.
- Topography: The geographical representation includes hills, rivers, and forests, which are critical for navigation.
- Legend and Scale: A legend provides a key to understanding the symbols, while a scale indicates distances accurately.
Among these elements, rock alignment diagrams serve as vital navigational aids. These diagrams depict the relationship between natural rock formations and the locations of buried treasures or points of interest.
Reading Rock Alignment Diagrams
Reading rock alignment diagrams requires a keen understanding of both cartographic principles and geological formations. e diagrams typically illustrate how certain rocks or natural features align with one another. By following these alignments, treasure seekers can pinpoint specific locations where treasures are believed to be buried.
Understanding Alignments
Geologists and treasure hunters alike utilize alignment diagrams to interpret the positions of rocks or formations. For example, a diagram might show that a particular boulder aligns with a distant mountain peak and a nearby river. This alignment may indicate that the treasure lies at a point where these lines intersect.
Common Symbols and Their Meanings
Common symbols you may encounter in these diagrams include:
- Triangles: Often represent markers or signposts that can be found in the field.
- Circles: Typically indicate areas of interest where treasure might be buried.
- Lines: Suggest direct pathways or alignments that could lead to the treasure.
These symbols, combined with the natural landscape they represent, form a navigational guide that can be invaluable for treasure hunters.
Case Studies of Successful Treasure Hunts
The practical application of reading rock alignment diagrams can be illustrated through case studies of treasure discoveries. One renowned example is the search for the lost treasures of the Spanish galleons that sank off the coast of Florida. In this particular case, treasure hunters utilized historical maps and alignment diagrams to focus their search on specific underwater rock formations.
Another notable case involved the famed “Cursed Treasure of Lima,†where explorers relied on detailed diagrams showing alignments of hills and rivers to unearth hidden gold. e successful hunts illustrate the significance of accurately interpreting rock alignment diagrams in the context of broader treasure hunting efforts.
Challenges in Interpretation
Despite their utility, reading rock alignment diagrams is not without challenges. One major concern is the potential for misinterpretation due to changes in the landscape over time. Natural erosion or human activities can alter the visibility and arrangement of rock formations, thus complicating alignment readings.
Importance of Contextual Knowledge
It is vital for treasure hunters to have contextual knowledge of the area in question, including its history, geology, and flora and fauna. Such knowledge enhances the accuracy of interpretation and increases the likelihood of successful treasure recovery.
Conclusion
Reading rock alignment diagrams in Spanish treasure maps presents a fascinating blend of history, geology, and adventure. By understanding their components, meanings, and practical applications, treasure hunters can navigate the complexities of these diagrams effectively. While challenges exist, thorough research and contextual knowledge can significantly mitigate potential misinterpretations.
For those interested in embarking on their treasure-hunting journey, it is crucial to combine these diagram-reading techniques with historical research and, where possible, engage with experts in cartography and geology to maximize the chances of success.