Exploring the unknown: how new technologies assist in mapping ancient tunnel systems.
Exploring the Unknown: How New Technologies Assist in Mapping Ancient Tunnel Systems
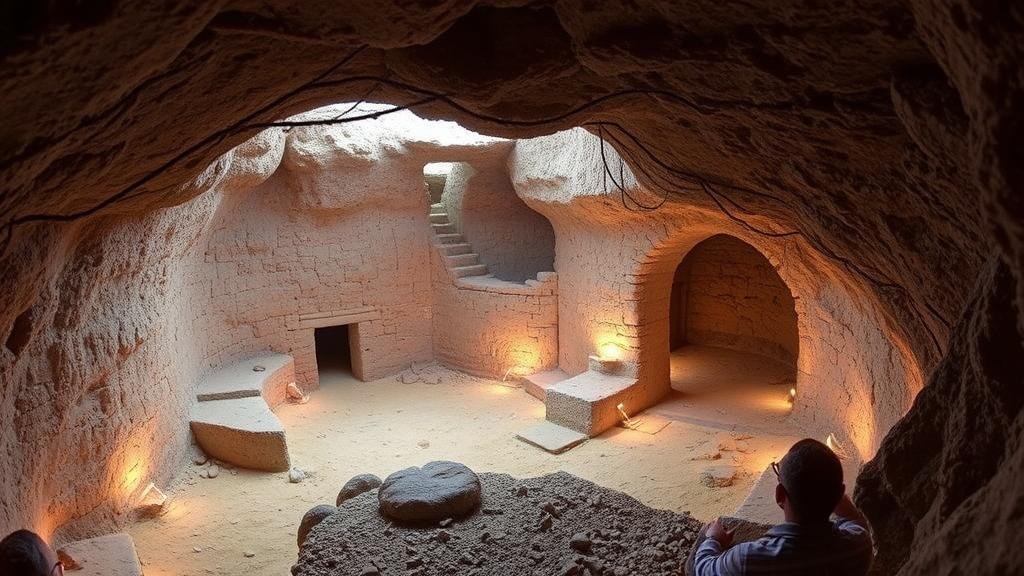
The quest to uncover the mysteries of ancient civilizations has long intrigued historians and archaeologists alike. Expanding knowledge about ancient tunnel systems, such as the intricate networks beneath cities like Rome, Paris, and Istanbul, has fundamentally changed our understanding of past societies. Recent technological advancements are enabling researchers to uncover and map these subterranean worlds with unprecedented clarity. This article delves into various cutting-edge technologies and methodologies that are revolutionizing the exploration of ancient tunnels.
The Importance of Ancient Tunnel Systems
Ancient tunnel systems served various purposes, from facilitating trade and transport to providing sanctuary during times of conflict. For example, the Catacombs of Paris, which date back to the late 18th century, originally served to manage the citys overflowing cemeteries. Today, they are one of the most iconic subterranean sites, attracting millions of visitors. Similarly, the 2,000-year-old aqueducts in Rome not only supplied water but also represent an engineering marvel of their time.
Technological Innovations in Tunnel Mapping
Recent advancements in technology have equipped researchers with powerful tools to explore ancient tunnels more effectively than ever before. Some of the most prominent methods include:
- Ground-Penetrating Radar (GPR): This non-invasive method uses radar pulses to image the subsurface and has been instrumental in discovering hidden chambers and structures. A prominent example is its use in the ancient city of Petra, Jordan, where GPR has revealed previously uncharted areas of the site.
- 3D Laser Scanning: By capturing millions of points in three dimensions, this technology allows for the detailed mapping of tunnel systems. In 2017, researchers used 3D laser scanning to document the extensive catacombs beneath Naples, Italy, revealing complex interconnections.
- Drone Technology: Drones equipped with cameras and LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) systems enable aerial surveys of tunnel entrances and systems, making it easier to chart difficult-to-access areas. In 2018, drones were employed in the Egyptian Valley of the Kings to help locate undiscovered tombs.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms analyze data from various mapping technologies to identify patterns and predict the location of unexplored sections. These models have been especially useful in the detection of hidden structures in the underground cities of Cappadocia, Turkey.
Case Studies of Ancient Tunnel Mapping
The Catacombs of Paris
The Catacombs of Paris are an extensive network that stretches over 200 miles underground. With the aid of GPR and 3D laser scanning, researchers have been able to create detailed maps of sections that are not accessible to the public. This has unveiled other potential chambers, leading to further archaeological exploration and the understanding of historical burial practices.
The Derinkuyu Underground City
Located in Cappadocia, Turkey, the Derinkuyu Underground City is a massive subterranean complex that could shelter thousands of people. Modern techniques, including AI analysis of GPR data, have highlighted additional levels of this ancient site, suggesting that it could be even larger than previously thought. e efforts have begun to paint a more comprehensive picture of how ancient societies practiced communal living and defense.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While the use of technology in archaeology offers exciting opportunities, it also presents numerous challenges. One primary concern involves the preservation of ancient sites. The intrusion of modern equipment can potentially damage fragile structures, necessitating careful planning and supervision during exploration.
Also, there are ethical considerations regarding the excavation and display of artifacts extracted from these sites. It is essential for archaeologists to engage local communities and stakeholders to honor the cultural heritage these tunnels represent.
Actionable Takeaways
As technology continues to evolve, the mapping of ancient tunnel systems stands at the forefront of archaeological innovation. Here are a few steps that enthusiasts and professionals can take to contribute to this exciting field:
- Stay informed about advancements in archaeological technology and their applications in the field.
- Engage with community organizations focused on the preservation of historical sites.
- Support funding for further research in ancient sites, ensuring that both technology and ethics are balanced.
Mapping ancient tunnel systems is not merely an academic endeavor; it is a vital part of understanding our collective history. With the aid of modern technologies, we are only beginning to scratch the surface of what these ancient networks have to offer.