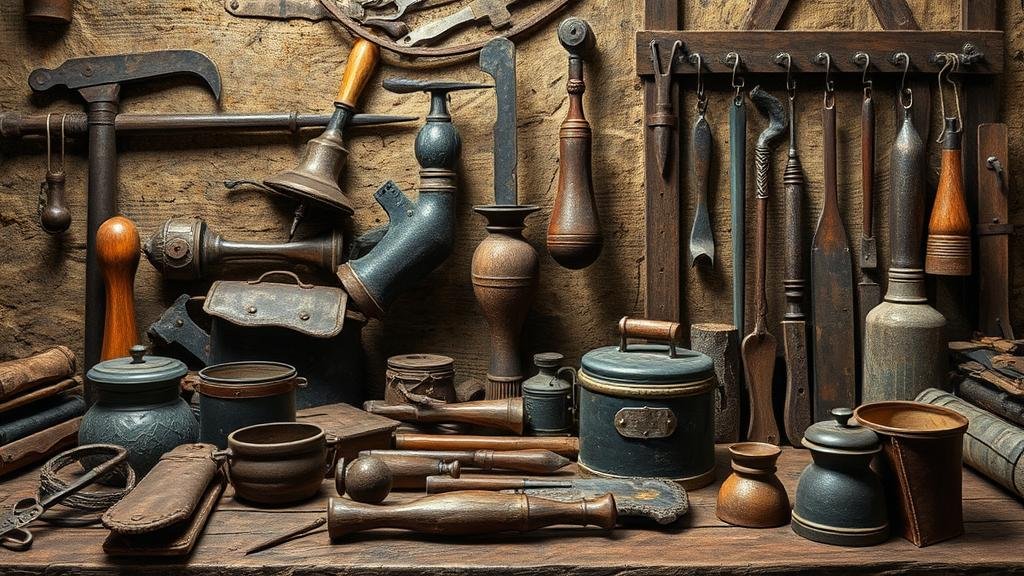
Exploring Forgotten Tanneries for Leatherworking Artifacts and Tools
Exploring Forgotten Tanneries for Leatherworking Artifacts and Tools
Leatherworking has been an essential craft throughout human history, with tanneries serving as the backbone of this trade. But, many tanneries have faded into obscurity, their artifacts and tools forgotten in the annals of time. This article explores the significance of these forgotten tanneries, the artifacts and tools associated with them, and the broader implications for the study of material culture and craftsmanship.
The Historical Context of Tanneries
Tanneries have existed since ancient times, with some of the earliest examples dating back to 3000 BCE in Mesopotamia. Historically, tanneries were vital for converting animal hides into leather, which was used for clothing, armor, and various tools. The methods involved varied across cultures, yet the essential processes of tanning have remained relatively consistent.
In medieval Europe, tanneries proliferated, especially in cities such as Florence, Italy, which became renowned for high-quality leather goods. The global leather market expanded significantly throughout the Industrial Revolution, with advancements in mechanization enabling large-scale production of leather goods.
Significant Forgotten Tanneries
Many tanneries that contributed significantly to local economies and cultures have now been abandoned or repurposed. Several noteworthy examples include:
- Belper, England: Once home to multiple tanneries during the 18th century, this towns leather goods were essential in the regional economy. Today, the remnants of these tanneries serve as historical landmarks.
- Fez, Morocco: The Chouara Tannery, operational since the 11th century, remains a pivotal historic site where traditional methods are still practiced. Its conservation raises awareness of leatherworking traditions that are often overlooked.
Artifacts and Tools of Leatherworking
The exploration of abandoned tanneries offers valuable insight into the tools and artifacts used in leatherworking. Notable items discovered at various sites include:
- Tanning Pit Tools: Tools used to immerse hides in tanning agents represented the shift from manual to more mechanical means of production.
- Staking Tools: Employed to soften leather, these tools illustrate how craftsmen prepared leather for different applications.
- Historical Records: Ledgers and invoices found in tanneries provide insights into the economic transactions of leather goods during specific periods.
The study of these artifacts allows researchers to trace technological advancements in leatherworking and the socio-economic conditions surrounding the industry.
Challenges in Research and Preservation
Despite the rich history and artifacts associated with forgotten tanneries, several challenges hinder research and preservation efforts:
- Environmental Degradation: Abandoned tanneries often suffer from neglect and environmental damage, which can destroy valuable artifacts.
- Lack of Documentation: Many tanneries did not maintain thorough historical accounts, making it difficult to piece together their contributions to leatherworking.
- Urban Development: Modern development often leads to the demolition of historic sites, further erasing the legacy of these tanneries.
Real-World Applications
The investigation of forgotten tanneries is not merely an academic pursuit; it has practical applications in fields such as:
- Cultural Heritage Conservation: Understanding the significance of tanneries can inform conservation efforts to protect leatherworking traditions.
- Education and Workshops: Reviving traditional techniques and tools can enhance educational programs in craft industries.
Such applications foster awareness regarding the importance of maintaining historical craftsmanship and encourage sustainable practices in the modern leather industry.
Conclusion and Actionable Takeaways
Exploring forgotten tanneries reveals not only the tools and artifacts of leatherworking but also the rich historical narratives embedded within these abandoned spaces. As researchers, craftspeople, and preservationists strive to document and conserve these remnants, there is a broader implication for understanding the cultural significance of craftsmanship in our societies.
For those interested in engaging with this research, consider the following actionable steps:
- Participate in local heritage projects focused on the conservation of historical tanneries and leatherworking techniques.
- Advocate for the protection of historical sites that house tanneries and encourage educational initiatives regarding traditional craftsmanship.
By preserving this integral part of human history, we ensure that the artistry and skills of leatherworking continue to be recognized and respected in contemporary society.