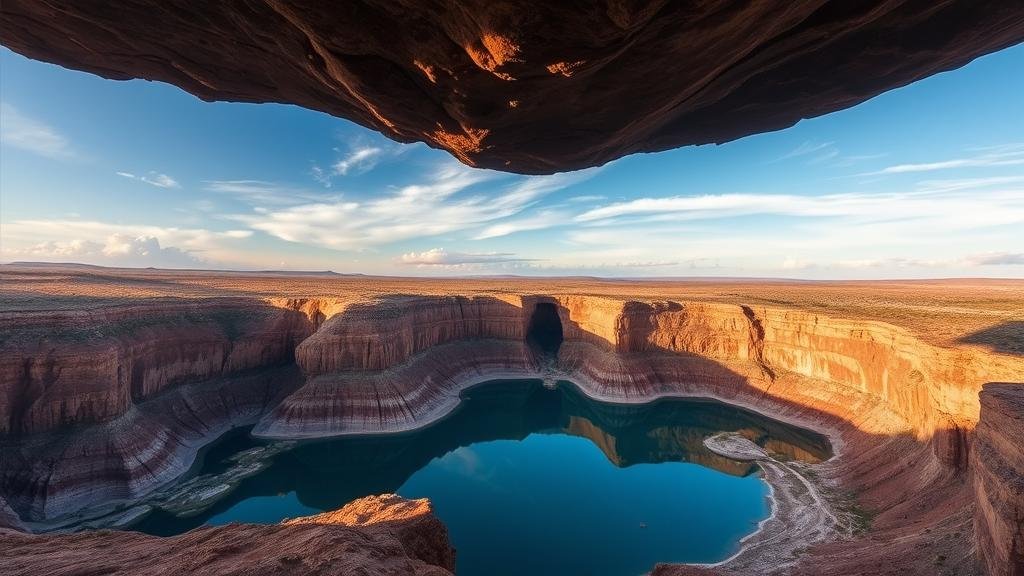
Investigating the “Hanging Lagoon,” a waterbody suspended between cliffs in South America that reflects the sky unnaturally.
Investigating the Hanging Lagoon: An Enigmatic Waterbody in South America
Nestled within the breathtaking Andean landscape, the Hanging Lagoon is a striking waterbody situated at altitudes exceeding 2,500 meters (8,200 feet) above sea level. This unique geological feature is found primarily in the remote regions of Peru and Bolivia, captivating visitors with its surreal ability to reflect the sky in vibrant, almost unnatural hues. Its origins and resulting ecosystems offer a profound insight into high-altitude hydrology and the delicate balance of local biodiversity.
Geological Formation
The Hanging Lagoon is the result of millions of years of geological processes, combining glacial activity with geological uplift that has formed steep cliffs and valleys. lagoon itself is believed to have been carved out by ancient glaciers during the last Ice Age, approximately 12,000 to 15,000 years ago. As the glaciers retreated, they left behind depressions that eventually filled with freshwater from melting snow and rain.
The unique location of the lagoon between sheer cliffs creates an isolated microclimate, allowing specific flora and fauna to thrive. As a result, the ecosystem around the lagoon is home to species that are not found in the surrounding areas, presenting researchers with a living laboratory for studying adaptation at high altitudes.
Unnatural Reflections: The Science Behind the Illusion
The enchanting display of vibrant reflections in the Hanging Lagoon is a byproduct of various physical and chemical properties of the water. high mineral content in the water, particularly high concentrations of magnesium and calcium, contributes to the waters unusual azure shades. Also, the lagoons shallow depth aids in creating a mirror-like surface, enhanced by the stark contrast of the surrounding cliffs and vegetation.
This phenomenon can be likened to looking into a polished piece of marble, where the surface reflects surroundings in a distorted yet captivating manner. During specific times of the day, when sunlight hits at a particular angle, the colors intensify, offering a visual spectacle that has led to its designation as a natural mirror.
Cultural Significance
Throughout history, local indigenous communities have revered the Hanging Lagoon, attributing spiritual significance to its existence. Often used as a site for rituals and offerings, the lagoon symbolizes a connection between the Earth and the heavens. The indigenous Qechua people, for instance, often visit the lagoon to conduct traditional ceremonies that invoke blessings for agricultural fertility and harmonious coexistence with nature.
Modern tourism has introduced new dynamics, with visitors flocking to witness the lagoons beauty firsthand. As of 2023, tourism to the region has increased by over 30% due to social media exposure and travel blogs highlighting such hidden gems. While this has brought economic benefits, it has also raised concerns about environmental sustainability and the preservation of cultural practices.
Environmental Considerations
Despite its ethereal beauty, the Hanging Lagoon faces potential threats from climate change and human activity. The regions delicate ecosystem is increasingly vulnerable to changes in temperature and precipitation patterns, which threaten to disrupt the delicate balance sustaining the lagoons flora and fauna.
According to a report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) released in 2022, the Andean regions are projected to face increased glacial melt, precipitation variability, and shifts in climate patterns. These changes can lead to alterations in the water levels of the lagoon, impacting both biodiversity and local agricultural practices.
Efforts made to monitor the health of the lagoon and implement sustainable tourism practices to mitigate environmental impacts. Local organizations and governments are also working on raising awareness among tourists regarding the need to respect this fragile ecosystem.
Actionable Takeaways
For those wishing to explore or study the Hanging Lagoon, here are some actionable guidelines:
- Practice responsible tourism: Always follow designated trails and respect local traditions and practices.
- Reduce your carbon footprint: Consider traveling during off-peak seasons to lessen overcrowding.
- Support local communities: Purchase souvenirs from local artisans to help sustain their livelihoods.
- Stay informed about environmental initiatives: Engage in dialogues about sustainability in ecotourism.
Investigating the Hanging Lagoon not only uncovers its natural wonders but also highlights the intricate relationship between cultural heritage and environmental stewardship. By promoting responsible interaction with this mystical landscape, we can ensure that it continues to inspire awe for generations to come.