Fluorite Fossil Mysteries: Glowing Crystals Found in Ancient Rock Layers
Fluorite Fossil Mysteries: Glowing Crystals Found in Ancient Rock Layers
Fluorite, a captivating mineral known for its vibrant colors and fluorescent properties, has long intrigued rockhounds and mineral collectors. When found in ancient rock layers, fluorite presents a fascinating case study that bridges geology, mineralogy, and even paleontology. This article explores the mysteries of fluorite fossils, detailing their origins, characteristics, and significance to both collectors and scientists.
What is Fluorite?
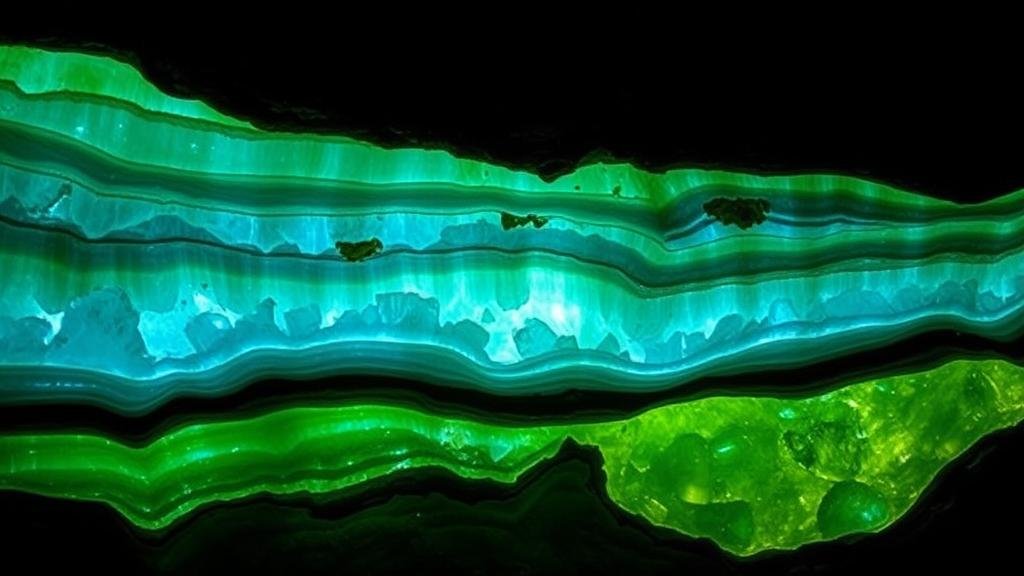
Fluorite, or calcium fluoride (CaF2), is a common yet stunning mineral. Known for its cubic crystal formation, fluorite often displays a range of colors–from deep greens and purples to vivid blues and yellows–often due to the presence of impurities. One of the most remarkable features of fluorite is its fluorescence; when exposed to ultraviolet light, it glows in an ethereal display, making it a prized specimen among collectors.
The Geological Context of Fluorite Fossils
Fluorite is typically found in sedimentary rocks, particularly in limestone and dolostone, as well as in igneous and metamorphic environments. Ancient rock layers incorporating fluorite have been dated back to different geological eras, making them age markers and revealing significant information about the Earth’s history.
For example, the famous fluorite deposits in the Illinois-Kentucky Fluorspar District are primarily found in rocks from the Mississippian period, approximately 359 to 323 million years ago. geological processes that led to the formation of fluorite in these deposits are complex, involving hydrothermal fluids that migrated through existing rock formations.
Unique Properties of Fluorite Fossils
Fluorite fossils can exhibit a range of unique properties that appeals to collectors:
- Fluorescence: As noted, fluorite’s ability to fluoresce can vary greatly among specimens. Some display strong fluorescence while others may show none at all, which can add to their collectible value.
- Color Zoning: Many fluorite specimens are characterized by zoning patterns where distinct color bands can be seen within the fluorite crystals, often revealing a beautiful gradient effect.
- Cubic Habits: The cubic crystal habit of fluorite is a distinctive feature that sets it apart from other minerals. This geometric perfection can make for striking specimens.
Significance to Rockhounds and Collectors
For rockhounds and mineral collectors, fluorite fossils offer both aesthetic and educational value. Collecting these specimens can provide insights into geological processes and the ecological conditions of ancient Earth. Also, the rarity of certain fluorite types can significantly increase their value.
Practical Tips for Collecting Fluorite Fossils
If youre eager to begin or expand your fluorite collection, consider the following tips:
- Research Locations: Identify and visit known fluorite-rich regions such as the Illinois-Kentucky Fluorspar District, the Southern California region, or the various Appalachian sites.
- Examine Conditions: Always consider the geological context when examining fluorite fossils. Look for signs of hydrothermal activity or sedimentary features that indicate the provenance of the specimen.
- Protect Your Specimens: Fluorite can be relatively soft (Mohs hardness of 4), making it more susceptible to scratches. Store specimens in a cool, dry place, and consider protective wrapping or display cases.
Real-World Applications of Fluorite
Beyond its aesthetic appeal, fluorite has numerous practical applications. It is widely used in the manufacturing of aluminum, gasoline, and uranium fuel. The fluorescence of fluorite is also leveraged in various scientific and industrial applications, such as in fluorescent lamps and glass production.
Conclusion
The mysteries of fluorite fossils lie not only in their radiant beauty but also in their profound geological significance. For rockhounds and mineral collectors, understanding the origins, properties, and applications of fluorite can enhance the collecting experience. By actively engaging with this fascinating mineral, collectors can uncover the stories embedded in ancient rock layers while contributing to a deeper understanding of Earth’s geological history.
Ultimately, exploring fluorite fossils offers a unique blend of adventure, discovery, and the joy of collecting that continues to captivate enthusiasts around the globe.