Recovering Tools and Trinkets in Old Timber Campsites
Recovering Tools and Trinkets in Old Timber Campsites
The recovery of tools and trinkets from old timber campsites is a fascinating endeavor that combines history, archaeology, and a deep appreciation for craftsmanship. This process is not only valuable for its potential to uncover historical artifacts but also for its role in ecological restoration and the understanding of timber industry practices. In this article, we will explore the methodologies used in recovering items from these sites, the significance of the findings, and the best practices to ensure both safety and environmental respect during the process.
The Historical Context of Timber Campsites
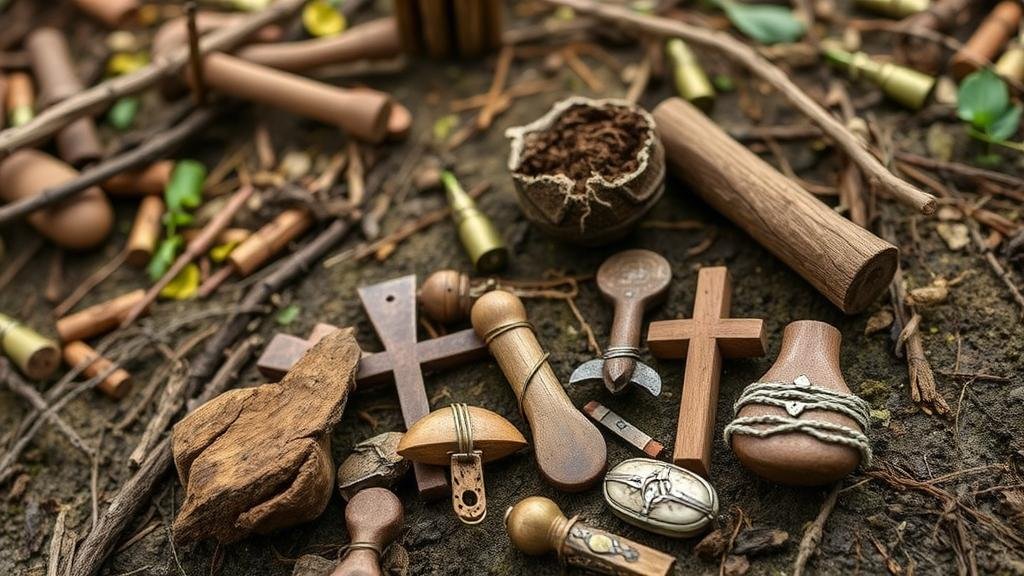
Timber camps were established in various regions during the Industrial Revolution and into the early 20th century, as demand for timber surged. e camps served as the bases for lumberjacks and sawmill workers, often comprising temporary structures made from milled wood. They typically included living quarters, workshops, and storage areas. The tools, trinkets, and personal items left behind provide invaluable insights into the daily lives of these workers. For example, the discovery of axes, wedges, and measuring tapes reveals not just the methods of logging but also the level of craftsmanship involved.
Methodologies for Recovery
The recovery of tools and trinkets from old timber camps requires a systematic approach that incorporates archaeological methods. Here are some core strategies:
- Site Assessment: Prior to any excavation, a thorough assessment is essential. This involves researching historical maps, documents, and local lore to identify possible timber campsite locations.
- Surface Survey: Conducting a surface survey aids in locating artifacts lying above ground. This non-invasive method allows for quick identification of tools or signs of human activity.
- Excavation Techniques: When digging is necessary, employing controlled excavation techniques ensures safe and respectful recovery. Systematic grid patterns are recommended to maintain context.
- Cataloging Finds: Each recovered item should be meticulously documented, including its location, depth, and condition. This information is vital for historical analysis and future research.
Significance of Findings
Recovering tools and trinkets can illuminate various aspects of timber camp life. For example, tools such as crosscut saws, felling axes, and various hand tools provide insight into the technological advancement in logging. Also, personal items, such as pocket watches and letters, can reveal the social dynamics and experiences of workers during that era.
According to a study conducted by the Society for Historical Archaeology, nearly 40% of surveyed timber camp sites revealed artifacts that date back to the late 1800s. The presence of these items not only supports historical narratives but also fosters community engagement and heritage conservation efforts.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
One prominent example is the recovery efforts conducted at the remnants of a 19th-century logging camp in Wisconsin. Excavations revealed a wealth of artifacts, including saw blades, horse tack, and personal items like an old harmonica. These findings contributed to the development of local historical exhibits and educational programs aimed at preserving the logging culture.
Similarly, in the Pacific Northwest, various volunteer groups have worked to recover artifacts from abandoned timber camps. Their efforts have led to the organization of community events, where findings are displayed, and the public can learn about the importance of logging history to regional identity.
Best Practices and Safety Considerations
While the allure of uncovering historical tools and trinkets is significant, it is crucial to follow best practices to ensure safety and environmental integrity. Key considerations include:
- Permitting: Always obtain the necessary permits for excavations, as many sites may be protected under local heritage laws.
- Environmental Impact: Be conscious of the ecological footprint. Avoid disturbing surrounding flora and fauna, and implement restoration practices post-excavation.
- Safety Gear: Wearing appropriate safety gear, such as gloves and hard hats, is essential when excavating in potentially hazardous environments.
Conclusion and Actionable Takeaways
The recovery of tools and trinkets from old timber campsites is more than simply retrieving artifacts; it is an ongoing exploration of our historical and cultural heritage. By employing systematic methodologies, respecting the environment, and documenting findings, individuals and organizations can contribute to a greater understanding of timber history.
As you embark on your recovery efforts, remember to:
- Conduct thorough research to identify potential campsite locations.
- Use careful excavation techniques to ensure both safety and contextual integrity.
- Engage with local communities to share findings and promote heritage awareness.
By following these guidelines, enthusiasts and researchers alike can responsibly uncover the rich stories hidden beneath the soil of old timber campsites.