Amber Fossil Fields: Finding Prehistoric Life Encased in Tree Resin
Amber Fossil Fields: Finding Prehistoric Life Encased in Tree Resin
Amber fossil fields represent a captivating intersection of geology, paleontology, and the curiosity of rockhounds and mineral collectors. These unique sites, where tree resin has hardened into amber, serve as time capsules of prehistoric life. This article delves into the formation of amber, the significance of fossil inclusions, and practical tips for collectors seeking treasures within these fields.
The Formation of Amber: A Natural Process
Amber is formed from the resin of ancient trees, primarily from species such as conifers, which thrived millions of years ago. process of amber formation begins when tree resin oozes out in response to injury or environmental stress. This sticky substance eventually hardens over time, undergoing a process known as polymerization. Geological conditions such as pressure and heat contribute to the transformation of resin into fossilized amber, a process that can take millions of years. In terms of measurements, amber can be dated back to around 310 million years ago in some regions, indicating the extensive timeline over which these fossils have formed.
The Significance of Fossil Inclusions
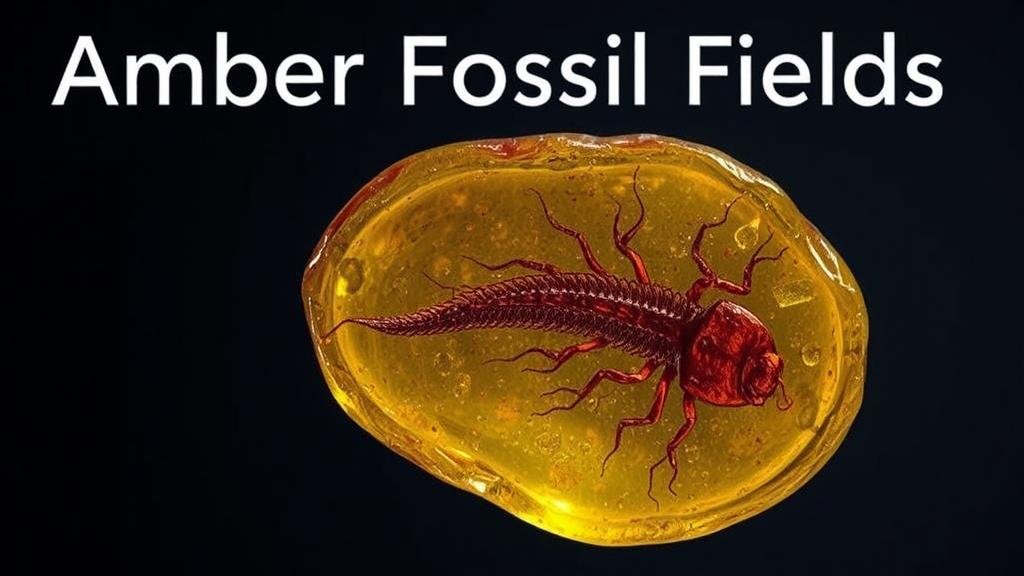
One of the most intriguing aspects of amber is its ability to preserve ancient life forms, known as inclusions. These can include:
- Insects, such as mosquitoes and ants
- Plant material, including leaves and flowers
- Small vertebrates, such as lizards or frogs
Fossil inclusions in amber provide invaluable insight into prehistoric ecosystems, as they reveal interactions between species and the environmental conditions of the time. For example, the discovery of a 99-million-year-old amber piece from Myanmar containing a feather has provided significant data about the evolution of birds and dinosaurs.
There are several notable amber deposits globally, each with unique characteristics and fossil inclusions. Some of the most renowned include:
- Baltic Amber: Originating from the Baltic Sea region, this amber is noted for its high clarity and ancient origins, dating back between 35 to 50 million years. The region is estimated to produce about 80% of the worlds amber supply.
- Dominican Amber: Found primarily in the Dominican Republic, this amber ranges from 20 to 40 million years old and is famous for its vibrant color and diverse inclusions, including insects that give insights into tropical ecosystems.
Tips for Rockhounds and Collectors
For those eager to explore amber fossil fields, here are practical tips to enhance your collecting experience:
- Research Locations: Identify areas known for amber deposits, such as beaches along the Baltic Sea or excavated sites in the Dominican Republic. Online forums and local mineral clubs can provide valuable insights.
- Use UV Light: Amber fluoresces under ultraviolet light, making it easier to identify authentic specimens. Carry a UV flashlight when hunting.
- Examine for Inclusions: When selecting pieces, look for amber with visible inclusions, as these often hold greater scientific and aesthetic value.
- Consider Ethical Collecting: Always follow local laws and regulations regarding fossil collecting to ensure sustainable practices and preserve natural heritage.
Real-World Applications and Discoveries
Studies of amber have led to substantial scientific discoveries. For example, through the examination of specimens, researchers have identified previously unknown species, expanded knowledge about ancient climates, and traced evolutionary lineages. In modern applications, amber is even seen as a modern treasure, often used in jewelry and art. Its popularity has resulted in a booming market, with high-quality pieces fetching thousands of dollars at auctions.
Conclusion: The Allure of Amber
Amber fossil fields offer a rich tapestry of history encased in hardened tree resin, captivating the attention of rockhounds and mineral collectors alike. With an understanding of how amber forms, the significance of inclusions, and some tips for collection, enthusiasts can embark on a rewarding journey into the past. Whether seeking unique specimens for personal collections or contributing to scientific research, the pursuit of amber remains a testament to natures artistry and the mysteries of prehistoric life.