Tracing Historical Cattle Ranch Sites for Agricultural Equipment Relics
Tracing Historical Cattle Ranch Sites for Agricultural Equipment Relics
The study of historical cattle ranch sites offers valuable insights into agricultural practices and technological advancements throughout history. This research article explores the methodology and significance of tracing these sites to uncover relics of agricultural equipment. Such relics not only illuminate the progression of ranching practices but also provide context for understanding regional agricultural development and economic history.
Historical Background of Cattle Ranching
Cattle ranching has a storied legacy in North America, particularly dating back to the Spanish colonization in the 16th century. introduction of cattle to the Americas marked the beginning of an evolutionary journey in agricultural practices. By the mid-19th century, cattle ranching was well-established, particularly in the Western United States. For example, the cattle industry underwent a transformation during the cattle drives of the 1860s to the 1890s, which facilitated the movement of cattle from Texas to railheads in Kansas for distribution across the nation.
Methodologies for Tracing Ranch Sites
Identifying and tracing historical cattle ranch sites involves a combination of archaeological and historical research methods.
- Archival Research: This entails examining historical documents, ranch records, newspapers, and land grants that provide evidence of ranching activities and equipment usage.
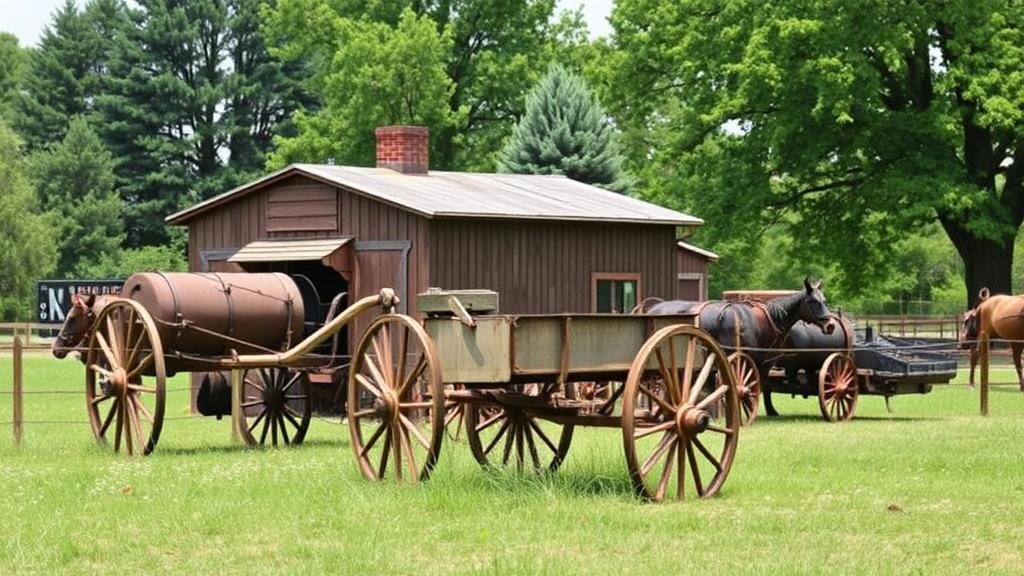
- Field Surveys: Systematic ground surveys can reveal remnants of agricultural equipment, such as plows, harrows, and other implements. Archaeological techniques such as excavation may also be employed to recover buried artifacts.
- Remote Sensing: Technologies such as aerial photography and LiDAR help identify structural remnants of ranch layouts and patterns that may not be visible from the ground level.
Significance of Agricultural Equipment Relics
The remnants of agricultural equipment uncovered at ranch sites are crucial for various reasons:
- Cultural Heritage: These relics serve as tangible links to the history of ranching communities, their economic practices, and daily operations. For example, the discovery of a 19th-century seed drill at a ranch in Colorado has provided insights into crop rotation practices used alongside cattle grazing.
- Technological Progress: The evolution of agricultural tools and machinery from simple hand tools to mechanized machinery illustrates advancements in technology. The proliferation of tractors in the 20th century, for instance, marked a shift from reliance on animal power.
- Environmental Impact: Understanding historical ranching practices through equipment relics helps to analyze their impact on soil management, land usage, and local ecosystems. For example, the transition from traditional plowing methods to more sustainable practices can be traced through archaeological findings.
Case Studies
Several case studies exemplify successful efforts in tracing historical cattle ranch sites and the agricultural relics they reveal.
- The King Ranch, Texas: Established in 1853, the King Ranch spans more than 825,000 acres. Archaeological studies have uncovered remnants of equipment such as vintage seeders and transportation wagons used during the ranchs operational periods. These findings have facilitated an understanding of agricultural evolution within the context of large-scale ranching.
- The Bar 6 Ranch, Montana: This historic ranch dating back to the late 1800s has yielded several significant relics, including barbed wire from the 1870s. Studies of these artifacts help contextualize land management strategies in the era of rapid cattle industry expansion.
Challenges in Tracing Ranch Sites
Tracing historical cattle ranch sites is not without its challenges:
- Land Development: Modern agricultural practices and urban development have often obliterated original ranch landscapes, making archaeological work more difficult.
- Funding and Resources: Many archaeological projects rely on grants and private donations, which can limit the scope of research.
- Historical Documentation: Inconsistent historical records and the oral history of ranching families may lead to gaps in knowledge about equipment use and ranch operations.
Conclusion
Tracing historical cattle ranch sites for agricultural equipment relics is a crucial endeavor that connects past practices with present understanding. As researchers employ innovative methodologies to uncover these artifacts, they provide significant contributions to our knowledge of agricultural history, technology evolution, and cultural heritage within rural America. Ongoing research will continue to reveal deeper insights into the practices of early ranchers, their challenges, and contributions to the agricultural landscape that we see today.
To wrap up, a focus on agricultural relics within historical ranch sites underscores the intertwined narrative of cattle ranching and the advancement of agricultural technology. As future research continues, it will be essential to address the challenges present in developing a comprehensive understanding of these historical sites.