How to Identify Historical Settlements Hidden by Rapid Jungle Growth
How to Identify Historical Settlements Hidden by Rapid Jungle Growth
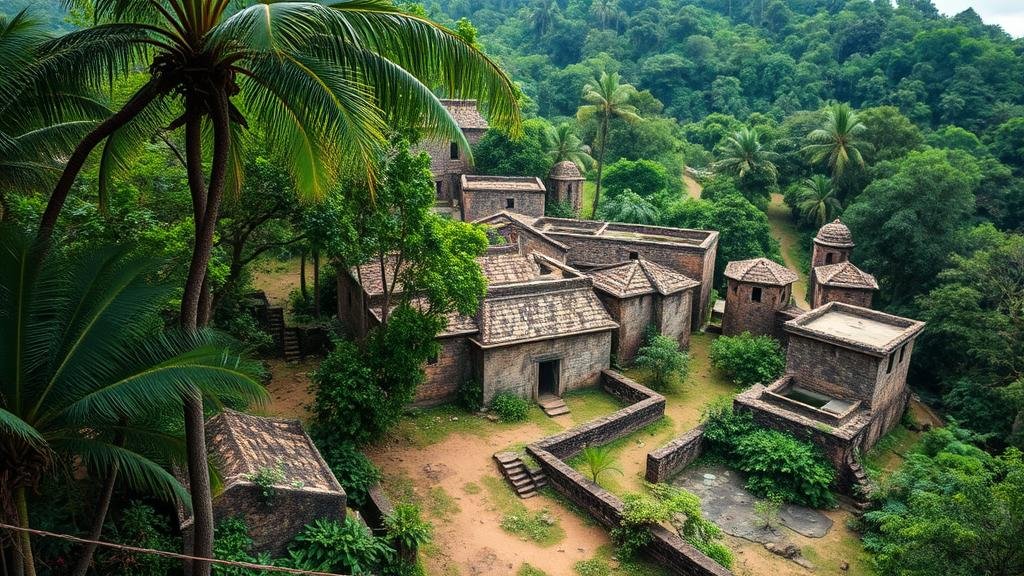
The exploration of historical settlements obscured by dense jungle can uncover invaluable insights into human civilization, culture, and architecture. This article delves into systematic methodologies, technologies, and case studies that aid in identifying these hidden sites, emphasizing the importance of interdisciplinary approaches in archaeology, anthropology, and environmental science.
Understanding the Challenges of Jungle Exploration
Dense jungles present unique challenges to archaeologists and historians, typically including:
- Vegetation Density: Thick canopies and underbrush obscure visibility, making traditional survey methods ineffective.
- Terrain Complexity: The rugged and often impenetrable landscape complicates physical access to potential sites.
- Environmental Factors: High humidity and rainfall can cause rapid deterioration of exposed artifacts.
These factors necessitate innovative techniques for the identification and documentation of hidden settlements.
Leveraging Remote Sensing Technology
Remote sensing technologies have revolutionized archaeological methodology, particularly in densely vegetated areas. Satellite imagery and aerial drones equipped with advanced sensors can penetrate thick foliage, revealing structures and patterns indicative of human habitation.
For example, the use of Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) has been significant in discovering ancient Maya cities in Guatemala. In 2018, LiDAR technology enabled researchers to map over 60,000 structures buried beneath the forest canopy, including roads, ditches, and pyramids, which were previously unknown.
Integrating Ground Surveys with Geophysical Techniques
While remote sensing provides invaluable initial data, comprehensive identification often requires ground surveys complemented by geophysical methods. Techniques such as Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) and magnetometry can help identify subsurface structures without extensive excavation.
- Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR): This method sends radar pulses into the ground and records reflected signals to create images of subsurface features.
- Magnetometry: This technique measures variations in the Earths magnetic field caused by changes in the soils magnetic properties, often indicating the presence of buried structures or artifacts.
Utilizing Historical and Ethnographic Records
Also to technological methodologies, historical texts and ethnographic studies can provide valuable clues regarding the location and nature of historical settlements. Journals, maps, and accounts from explorers and indigenous communities can reveal long-lost towns, trade routes, and cultural practices.
For example, the detailed notes of 19th-century explorers in the Amazon basin have helped locate ancient settlements associated with the Inca and pre-Inca civilizations. Coupled with modern methodologies, these historical accounts form a baseline for investigation.
Case Studies of Successful Discoveries
Several notable case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of these combined methods:
- Angkor Wat, Cambodia: Dense jungle growth concealed portions of this UNESCO World Heritage site until re-discovery through aerial surveys and LiDAR mapping revealed extensive urban planning.
- Cahokia Mounds, Illinois, USA: Archaeological investigations, supported by historical documentation and geophysical methods, unveiled a sophisticated urban center formerly obscured by vegetation.
Future Directions and Sustainable Practices
The exploration of hidden historical settlements must balance archaeological interests with the preservation of delicate ecosystems. Sustainable practices include:
- Application of Non-Invasive Techniques: Prioritizing archaeological methods that minimize environmental disturbance ensures the long-term preservation of both cultural and ecological heritage.
- Collaboration with Local Communities: Engaging indigenous communities in research can provide critical ecological knowledge and facilitate better protection of heritage sites.
Conclusion and Actionable Takeaways
The identification of historical settlements hidden by rapid jungle growth hinges on a multifaceted approach combining technological innovation and traditional methods. By integrating remote sensing, ground surveys, and historical records, researchers can uncover significant cultural sites. Plus, a commitment to sustainable practices ensures these discoveries are preserved for future generations.
So, for researchers, archaeologists, and conservationists, the key takeaway is the importance of collaboration across disciplines and integrating modern technology with historical knowledge to unlock the secrets of our shared past.